会话:追踪独立对话
在介绍之后,让我们深入探讨Session。回想"对话线程"的概念。就像你不会每次发短信都从头开始一样,智能体需要从持续互动中获取上下文。Session是ADK中专门用于追踪和管理这些独立对话线程的对象。
Session对象
当用户开始与您的智能体交互时,SessionService会创建一个Session对象(google.adk.sessions.Session)。该对象作为容器,保存与特定聊天线程相关的所有内容。以下是其关键属性:
- 标识(
id,app_name,user_id):对话的唯一标签id:该特定对话线程的唯一标识符,对于后续检索至关重要app_name:标识该对话属于哪个智能体应用user_id:将对话与特定用户关联
- 历史记录(
events):按时间顺序排列的所有交互(Event对象——用户消息、智能体响应、工具操作) - 会话数据(
state):存储仅与该特定持续对话相关的临时数据,作为交互期间智能体的便笺。我们将在下一节详细介绍如何使用和管理state - 活动追踪(
last_update_time):时间戳,表示该对话线程最后一次添加事件的时间
示例:检查会话属性
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService, Session
# Create a simple session to examine its properties
temp_service = InMemorySessionService()
example_session: Session = temp_service.create_session(
app_name="my_app",
user_id="example_user",
state={"initial_key": "initial_value"} # State can be initialized
)
print(f"--- Examining Session Properties ---")
print(f"ID (`id`): {example_session.id}")
print(f"Application Name (`app_name`): {example_session.app_name}")
print(f"User ID (`user_id`): {example_session.user_id}")
print(f"State (`state`): {example_session.state}") # Note: Only shows initial state here
print(f"Events (`events`): {example_session.events}") # Initially empty
print(f"Last Update (`last_update_time`): {example_session.last_update_time:.2f}")
print(f"---------------------------------")
# Clean up (optional for this example)
temp_service.delete_session(app_name=example_session.app_name,
user_id=example_session.user_id, session_id=example_session.id)
(注意:上述状态仅为初始状态。状态更新通过事件实现,详见状态章节。)
使用SessionService管理会话
通常不直接创建或管理Session对象,而是使用SessionService。该服务作为核心管理器,负责对话会话的整个生命周期。
其主要职责包括:
- 启动新对话:用户开始交互时创建新的
Session对象 - 恢复现有对话:检索特定
Session(使用其ID)使智能体能从中断处继续 - 保存进度:将新交互(
Event对象)追加到会话历史记录中。这也是会话state更新的机制(详见状态章节) - 列出对话:查找特定用户和应用的活跃会话线程
- 清理:在对话结束或不再需要时删除
Session对象及其关联数据
SessionService实现
ADK提供不同的SessionService实现,允许选择最适合需求的存储后端:
-
InMemorySessionService- 工作原理:直接在应用内存中存储所有会话数据
- 持久性:无。应用重启后所有对话数据都会丢失
- 要求:无需额外配置
- 适用场景:快速测试、本地开发、示例以及不需要长期持久性的场景
-
DatabaseSessionService- 工作原理:连接关系型数据库(如PostgreSQL、MySQL、SQLite)将会话数据持久存储在表中
- 持久性:有。数据在应用重启后仍保留
- 要求:配置好的数据库和
sqlalchemy库(pip install google-adk[database]) - 适用场景:需要可靠、持久存储且自行管理的应用
-
VertexAiSessionService- 工作原理:通过API调用使用Google Cloud的Vertex AI基础设施进行会话管理
- 持久性:有。数据由Google Cloud可靠且可扩展地管理
- 要求:Google Cloud项目、适当权限、必要SDK(
pip install google-adk[vertexai])以及推理引擎资源名称/ID - 适用场景:部署在Google Cloud上的可扩展生产应用,特别是需要与其他Vertex AI功能集成的场景
# Requires: pip install google-adk[vertexai] # Plus GCP setup and authentication from google.adk.sessions import VertexAiSessionService PROJECT_ID = "your-gcp-project-id" LOCATION = "us-central1" # The app_name used with this service should be the Reasoning Engine ID or name REASONING_ENGINE_APP_NAME = "projects/your-gcp-project-id/locations/us-central1/reasoningEngines/your-engine-id" session_service = VertexAiSessionService(project=PROJECT_ID, location=LOCATION) # Use REASONING_ENGINE_APP_NAME when calling service methods, e.g.: # session_service.create_session(app_name=REASONING_ENGINE_APP_NAME, ...)
选择合适的SessionService是定义智能体对话历史和临时数据存储及持久化方式的关键。
会话生命周期
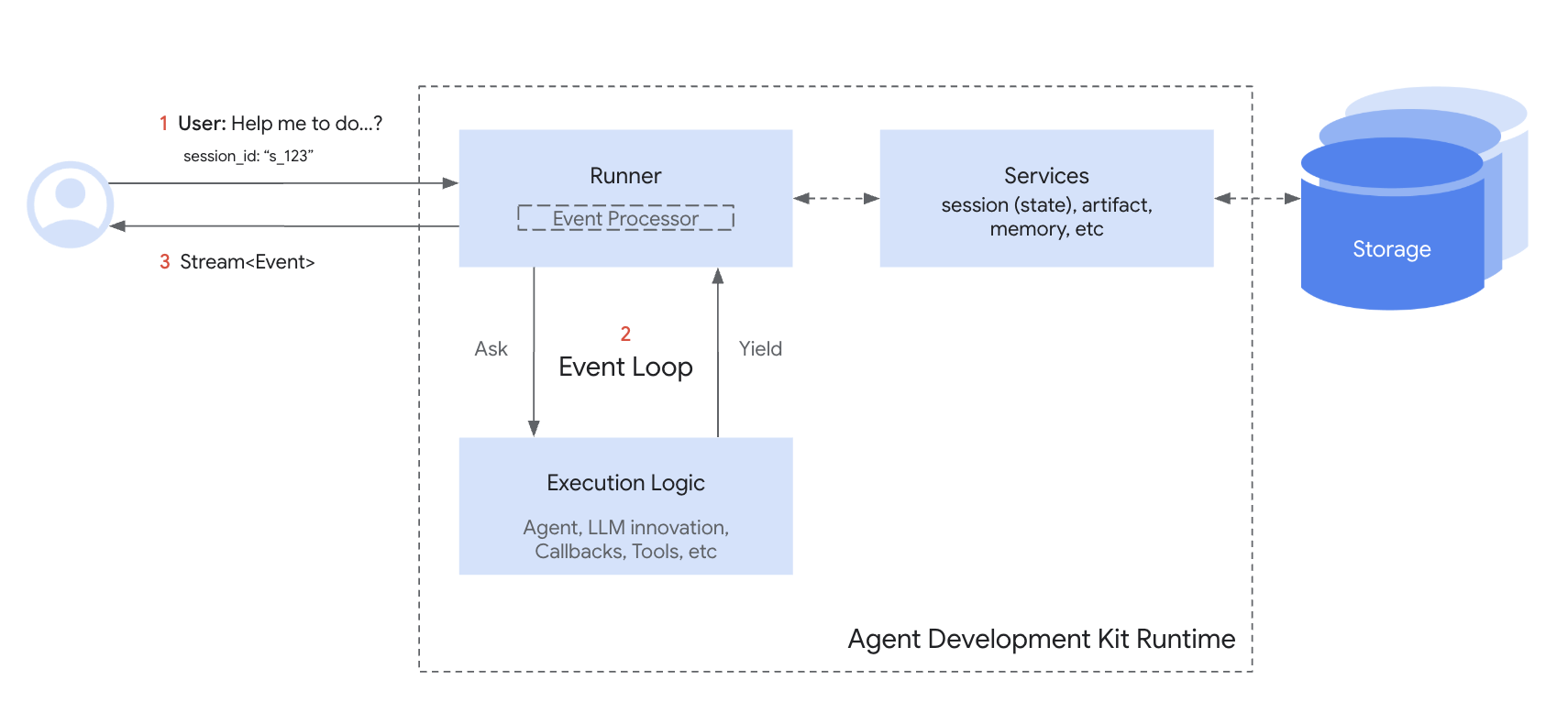
以下是Session和SessionService在对话轮次中协同工作的简化流程:
- 启动或恢复:用户发送消息。应用的
Runner使用SessionService来create_session(新聊天)或get_session(检索现有会话) - 提供上下文:
Runner从服务获取适当的Session对象,为智能体提供访问其state和events的权限 - 智能体处理:智能体使用当前用户消息、其指令以及可能的会话
state和events历史记录来决定响应 - 响应与状态更新:智能体生成响应(并可能标记要在
state中更新的数据)。Runner将其打包为Event - 保存交互:
Runner调用session_service.append_event(...),传入Session和新Event。服务将Event添加到历史记录中,并根据事件信息更新存储中的会话state。会话的last_update_time也会更新 - 准备下一轮:智能体响应发送给用户。更新后的
Session由SessionService存储,准备下一轮交互(通常使用get_session,从步骤1重新开始循环) - 结束对话:对话结束时,理想情况下应用应调用
session_service.delete_session(...)清理存储的会话数据
这个循环展示了SessionService如何通过管理与每个Session对象关联的历史记录和状态来确保对话连续性。